Featured Science
In the beginning of 2020, when SARS-CoV-2 virus infection started affecting the countries globally, nobody had imagined that a pandemic of such a scale, which infected more than 440 million people and resulted in >6 million deaths will affect all of us. It was a challenge for the nations to stand up and fight against this pandemic. India, as a nation, encouraged its scientific community to develop centres and facilities to study SARS-CoV-2 infections and help in better diagnostics, assay development and also contribute to vaccine research and development. Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI), Faridabad played a key role in basic, clinical and translational research.

1. Clinical Research
(i) DBT Consortium
THSTI is the lead coordinator of DBT’s Consortium for COVID-19 research, a multi-institutional platform for developing a clinical cohort of patients with COVID-19, collecting bio specimens, and conducting vaccine effectiveness and re-infection studies.
(ii) Establishment of clinical cohorts for COVID-19
These cohorts are being studied for understanding durability of immunity, risk of re-infection, long COVID-19, waning of immunity and break through infection. The following important immunological findings were observed in longitudinal serological studies.
- All with severe disease, 89.6 per cent with mild to moderate infection and 77.3 per cent of asymptomatic participants showed seroconversion (IgG antibodies against RBD antigen).
- Seropositivity decreased by 22 per cent between 6-10 weeks and six months from onset of illness
- Decreasing trend seen across all the three subgroups viz., asymptomatic, mild/moderate and severe.
(Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2021 May 18; 105(1):66-72. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.21-0164.)
(iii) Vaccine effectiveness
- A multi-institutional team of Indian researchers led by THSTI evaluated the real-world vaccine effectiveness of Covishield during the SARS-CoV-2 infection surge between April and May 2021, in India. The vaccine effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 infection in fully vaccinated individuals was found to be 63 per cent. The vaccine effectiveness of complete vaccination against moderate-to-severe disease was much higher at 81 per cent. More importantly, the scientists also observed that the spike-specific T-cell responses were conserved against both the delta variant and wild-type SARS-CoV-2.
(Lancet Infect Dis. 2021 Nov 25:S1473-3099(21)00680-0. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00680-0.)
- In a cross-sectional study, the ability of vaccine (Covishield and Covaxin) and natural infection induced antibodies to neutralise Omicron variant in a live virus neutralisation assay was carried out. Significant reduction in the neutralising ability of both vaccine-induced and vaccine plus infection-induced antibodies was observed for Omicron variant, which might explain immune escape.
(EBioMedicine. 2022 Mar 15;78:103938. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.103938.)
(iv) Durability of humoral immune response at least six months after complete vaccination with Covishield or Covaxin
In a cross-section observational study conducted between November 2021 and January 2022, it was observed that anti-RBD IgG was persistent in 85 per cent of participants even beyond a median of eight months after complete vaccination. The antibody concentrations were significantly higher in those with hybrid immunity. This implies that humoral immunity may last longer due to heterologous antigenic exposure following vaccination and natural infection emphasising the need for contextualising the booster policy.
(Pre-print: medRxiv 2022.02.23.22271381; doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.02.23.22271381)
(v) Longitudinal cohort study to evaluate outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 virus variants
THSTI as the coordinating centre along with a network of hospitals across the country are conducting a study to evaluate the severity and outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection and correlation of clinical outcomes with virus variants. The study is ongoing and will help in answering the following questions:
- Is the severity of disease caused by new variants of SARS-CoV-2 different compared to the wild type?
- Is the outcome of COVID-19 due to new variants worse than that due to wild type?
- What are the long-term sequelae of COVID-19?
(vi) Biorepository facility at THSTI
It is a unique resource of well phenotyped COVID-19 cases that followed longitudinally since 2020 and houses more than 5000 corona positive samples. This bioresource has been helping both the academia and industries in the development of diagnostic kits and vaccine development.
2. Vaccine Development
(i) Support to industry
THSTI contributed immensely in the clinical trials/development of vaccines for COVID-19 including Dr Reddy’s (Sputnik), ZydusCadilla (ZyCoV-D), and Biological E (Corbevax) and entered into an international collaboration with Nanogen Pharmaceutical Biotechnology JSC, a Vietnamese pharmaceutical company, which is developing a new vaccine for COVID-19.
(ii) Indigenous vaccine work
- THSTI in collaboration with Panacea Biotec has received CEPI funding for a project ‘to develop a multi-epitope, nanoparticle-based broadly protective Beta coronavirus candidate vaccine.’
- Researchers at THSTI are working towards developing mRNA and subunit vaccines for COVID-19, which have shown promising results.
3. Diagnostics
(i) In-house diagnostics
For newer in-house diagnostics against SARS-CoV-2 amidst global shortage, THSTI developed technologies, which were transferred to industries as given in Table 1. THSTI developed an antibody ELISA technology, which has been transferred to industry and used for serosurveillance in Karnataka. THSTI also developed the first APTAMER-based SARS-COV-2 detection assay targeting Spike and Nucleocapsid antigens that has also been transferred to industry.
S. No. | Technology | Licensee |
ELISA (using receptor binding domain of spike protein) to detect IgG antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 | Xcyton Diagnostics Limited | |
Conventional PCR compatible-DNAzyme-based visual detection method for SARS-CoV-2 as an alternative to real-time PCR-based assay | Genei Labs | |
Panel of aptamers specific to SARS-CoV-2 spike protein | Molbio Diagnostics | |
Panel of aptamers specific to SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein | Cambrain Bioworks LLP |
Technologies developed by THSTI w.r.t. SARS-CoV-2 and transferred to industries
Antibody ELISA kit transferred to Xcyton Diagnostics Limited
(ii) RT-PCR Tests
Bioassay Laboratory (BL) has tested more than 1,72,000 clinical samples for SARS-CoV-2 using RT-PCR. Out of these samples, more than 33,000 samples were tested by India's first mobile infectious disease diagnostic lab (I-lab) managed by THSTI.
(iii) Kit Validations and Training
BL has performed 28 COVID-19 kit validations to date. In collaboration with Foundation for Innovative New Diagnostics (FIND), BL trained manpower for COVID-19 from various organisations for capacity building.
(iv) Genome sequencing
THSTI is a member of INSACOG and has sequenced 385 whole genomes of SARS-CoV-2 isolated from COVID-19 patients living in Haryana and other states of India. The sequences are deposited in the IHIP portal, INSACOG database and GISAID database.
4. Animal Models
THSTI was the first institution in the country to establish two models of SARS-CoV-2 infections in hamster and ACE2 transgenic mice models. These models were provided to industries (Dr Reddy’s, ZydusCadilla, Biological E, etc.) and academia (Ministry of Ayush, IGIB, ICGEB, RCB, etc.) for pre-clinical vaccine testing and anti-viral screening.
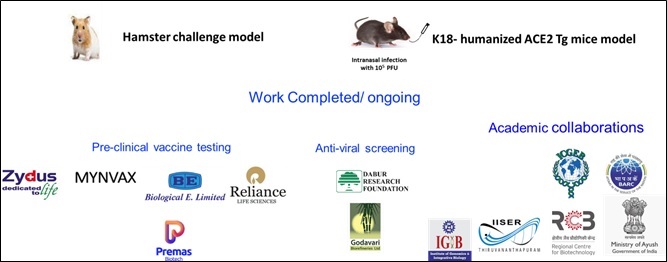
Animal models provided to companies and academia for vaccine development
5. Establishment of Assays for Immune Correlates of Protection
(i) The immunology core lab of THSTI provided a cellular assay platform for determining the immunogenicity of COVID-19 vaccines. It provides the following T cell assays:
- SARS-CoV-2 specific T cell proliferation
- SARS-CoV-2 specific T cell cytokine production by ELISA, ELISPOT/FLUROSPOT and intracellular staining
- SARS-CoV-2 specific antigen induced marker (AIM) assay
(ii) Live virus neutralisation assays are essential to test the efficacy of vaccines and therapeutic molecules. The infectious disease research facility of THSTI carried out neutralisation assays for many vaccine developers and vaccine effectiveness studies.
(iii) BL became a part of Coalition of Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI) centralised network labs for COVID-19 vaccine testing, the only lab in India with such distinction. The laboratory has developed in-house assays for SARS-CoV-2 by using WHO reference standard for validation.
6. Therapeutic monoclonal antibodies
THSTI has developed potential therapeutic monoclonal antibodies against COVID-19, which have immense therapeutic potential to neutralise the current circulating variant of concerns.
Extensive work done by THSTI on SARS-CoV-2 has helped in the approval of vaccines and diagnostic tests in the country. The in-house strong product pipeline on candidate vaccines, therapeutic antibodies and high sensitivity diagnostic assays are on the horizon to meet the challenge. The work done on understanding the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 after natural infection and vaccination should help in preparing an appropriate national policy on vaccination.
Contact info:
Mr. M V Santo, santo@thsti.res.in
Dr. Soma Patnaik, soma@thsti.res.in



